- The breast, or mammary gland, is a paired, modified sweat gland located on the anterior thoracic wall.
- Its primary biological function is to produce and secrete milk to nourish infants, a process known as lactation.
- The breast is composed of glandular tissue (lobes and lobules), connective tissue (including fat), ducts that transport milk to the nipple, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
- In Breast (Mammary Gland) have the breast undergoes significant changes during puberty, pregnancy, and lactation, while in males, it remains rudimentary.
Position:
- The breasts, or mammary glands, are located on the anterior chest wall, overlying the pectoralis major muscles.
- They are present in both males and females but are more developed and functional in females.
Structure:
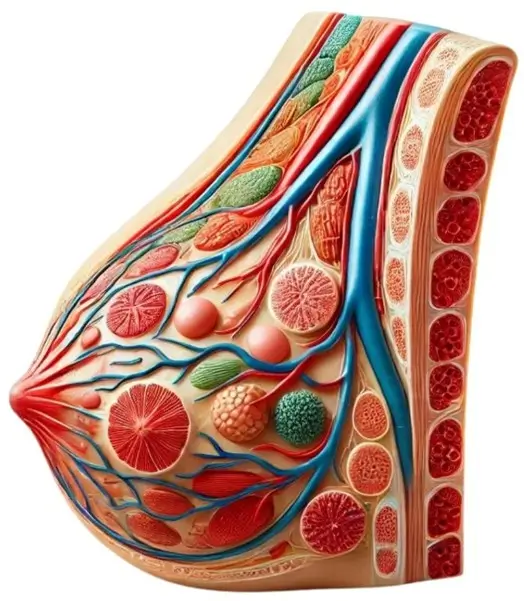
- Each breast is composed of glandular tissue (lobules and ducts) and supportive connective tissue (fibrous and fatty tissue).
- The glandular tissue is organized into lobules, which are small sacs that produce milk during lactation.
- These lobules are connected to a network of ducts that transport milk to the nipple.
- The nipple is surrounded by a pigmented area called the areola, which contains sebaceous glands that secrete lubricating and protective substances.
Development:
- Breast development occurs in stages, mainly during puberty, under the influence of hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone. The stages of breast development include:
- Prepubertal stage:
- Breasts are small and undeveloped in both males and females.
- Budding stage:
- Estrogen stimulates the growth of the breast bud, involving the development of the duct system and some enlargement of the breast tissue.
- Continued growth:
- Throughout puberty, the breast tissue continues to grow and develop, with the duct system branching and expanding.
- The fatty and fibrous connective tissues also increase.
- Mature stage:
- After puberty, the breasts reach their adult size and shape. However, their size and composition may change throughout a woman’s life due to factors such as hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, and lactation.
Function:
- The primary function of the breasts is to produce and secrete milk for the nourishment of infants.
- This process, called lactation, is regulated by hormones such as prolactin and oxytocin.
- During lactation, milk is produced in the lobules, transported through the ducts, and released through the nipple when the infant suckles.
- In addition to lactation, breasts also:
- Play a role in sexual arousal.
- Serve as secondary sexual characteristics, contributing to a person’s overall body image and self-perception.

