Cholestyramine is a bile acid sequestrant used to lower LDL cholesterol by binding bile acids in the intestine.
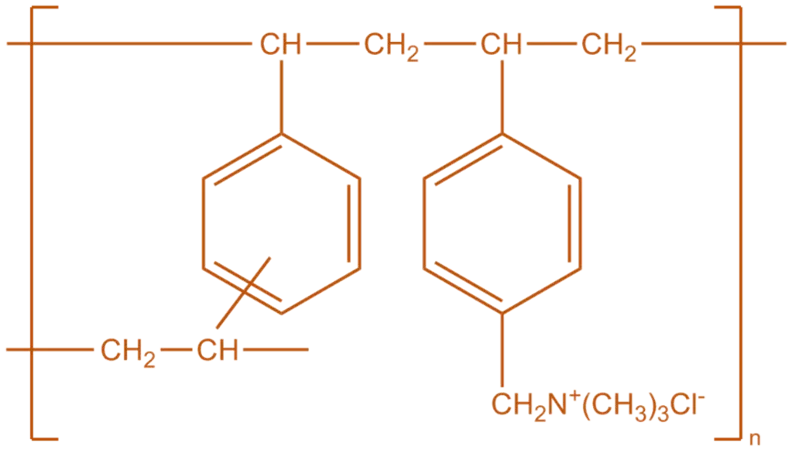
Structure of Cholestyramine
- Cholestyramine is a bile acid sequestrant composed of a cross-linked polymer of divinylbenzene and polyethylene oxide, functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups.
- Chemical Formula: (C₁₂H₁₅NO)n·Cl⁻
Mode of Action
- Bile Acid Sequestration: Binds bile acids in the intestine, preventing their reabsorption.
- Cholesterol Reduction: Forces the liver to convert more cholesterol into bile acids, thereby lowering blood cholesterol levels.
- LDL-C Lowering: Reduces low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by decreasing hepatic cholesterol synthesis.
Uses
- Hypercholesterolemia: Lowers LDL-C and total cholesterol levels.
- Pruritus Associated with Cholestasis: Alleviates itching by binding bile acids.
- Bile Acid Diarrhea: Manages chronic diarrhea caused by bile acid malabsorption.
- Fibromyalgia: Sometimes used off-label for pain management.

