HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes.
HACCP can be applied at all stages of the food chain, from production to consumption.
Objective:
To prevent food safety hazards by identifying critical control points in the food production and processing chain.
To systematically assess and manage biological, chemical, and physical risks in food products.
To ensure continuous improvement and compliance with international food safety protocols.
To empower food businesses to take control and ensure the safety of their food products at every stage of production.
Functions:
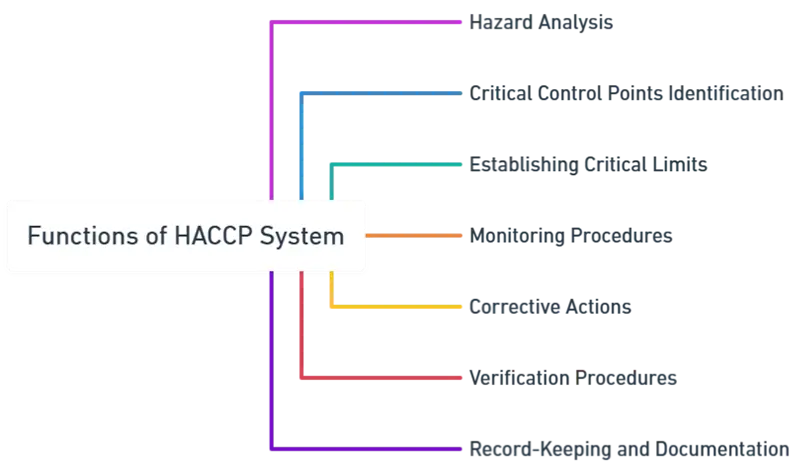
1. Hazard Analysis:
The first step in a HACCP system involves conducting a thorough analysis of potential food safety hazards, so that these hazards can be effectively managed at different stages of the production process.
2. Critical Control Points Identification:
Identifying points in the process where identified hazards can be controlled or eliminated.
These points, known as Critical Control Points (CCPs), are essential for ensuring product safety.
3. Establishing Critical Limits:
For each CCP, there are established critical limits that must be met to ensure that each hazard is under control.
These might include temperatures, pH levels, salt concentration, and more.
4. Monitoring Procedures:
Developing and implementing procedures for monitoring CCPs to ensure that each critical limit is being met.
This often involves scheduled testing and observation.
5. Corrective Actions:
Establishing protocols for corrective actions to be taken when monitoring indicates that a particular CCP is not under control.
6. Verification Procedures:
Implementing procedures to verify that the HACCP system is working effectively.
This can include additional testing, inspection, and review of records.
7. Record-Keeping and Documentation:
Keeping detailed records of all aspects of the HACCP plan, including hazard analyses, monitoring of CCPs, corrective actions taken, and verification activities.
This documentation ensures that the system is traceable and accountable.
While AGMARK focuses on certifying the quality of agricultural products through set standards and inspections, HACCP provides a comprehensive system aimed at ensuring food safety through the identification and control of potential hazards throughout the food production process. Both play vital roles in their respective areas to promote the safety and quality of food products.
