- The human body is a complex, organized structure consisting of various levels, from the smallest unit of life to the most complex systems.
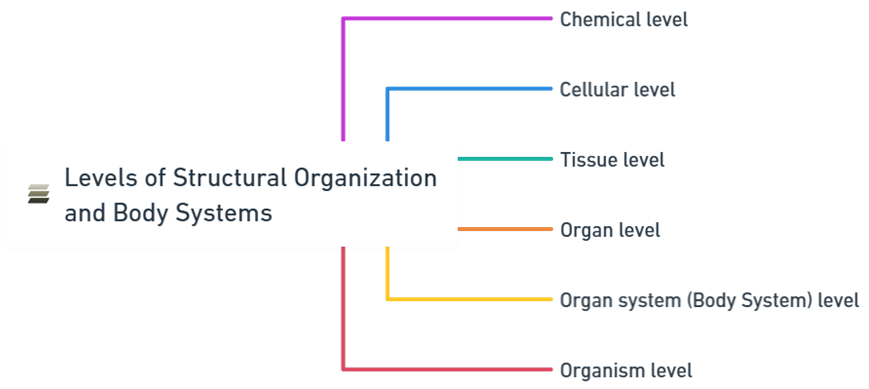
The levels of structural organization can be categorized as follows:
1. Chemical level:
- This is the most basic level, encompassing atoms and molecules.
- Atoms, the smallest units of matter, combine to form molecules, which are the building blocks for cells and their components.
- Examples include water, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
2. Cellular level:
- Cells are the smallest functional units of life, each with a specific role in the body.
- They contain various organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, which perform specialized tasks to ensure the cell’s proper functioning.
3. Tissue level:
- Tissues are groups of similar cells working together to perform specific functions.
- There are four primary types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
4. Organ level:
- Organs are structures composed of two or more tissue types that work together to perform specific functions.
- Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys.
5. Organ system (Body System) level:
- The body consists of 11 major organ systems, each responsible for specific physiological functions:
A. Integumentary System:
- Components: Skin, hair, nails, and glands.
- Function: Protects the body, regulates temperature, and provides sensory information.
B. Skeletal System:
- Components: Bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints.
- Function: Provides structure, protects organs, anchors muscles, and stores minerals.
C. Muscular System
- Components: Skeletal muscles, tendons.
- Function: Facilitates movement, maintains posture, and produces heat.
D. Nervous System
- Components: Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, sensory organs.
- Function: Controls body activities with electrical signals, processes sensory information, and coordinates responses.
E. Endocrine System
- Components: Glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, and pituitary gland.
- Function: Secretes hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
F. Cardiovascular System
- Components: Heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries).
- Function: Transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
G. Lymphatic/Immune System
- Components: Lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, thymus, spleen, tonsils.
- Function: Defends against infection, returns leaked fluids to the blood, and absorbs dietary fats.
H. Respiratory System
- Components: Lungs, trachea, bronchi, nasal cavity, larynx.
- Function: Provides oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide.
I. Digestive System
- Components: Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder.
- Function: Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
J. Urinary System
- Components: Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra.
- Function: Removes waste products from the blood, regulates blood volume, and maintains electrolyte balance.
K. Reproductive System
- Male: Testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, penis.
- Female: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina.
- Function: Produces gametes (sperm in males, eggs in females), supports fetal development in females.
Basic life processes
- Basic life processes are the essential functions that all living organisms, including humans, must perform to maintain life and ensure survival.
- These processes are interdependent and necessary for maintaining homeostasis – the stable internal environment of the organism
- these are all the details of levels of structural organization and body systems
