- A neuron, or nerve cell, is the fundamental unit of the nervous system responsible for processing and transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals.
- Neurons are the building blocks of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body.
- While there are various types of neurons with specialized functions, they all share a common structure:
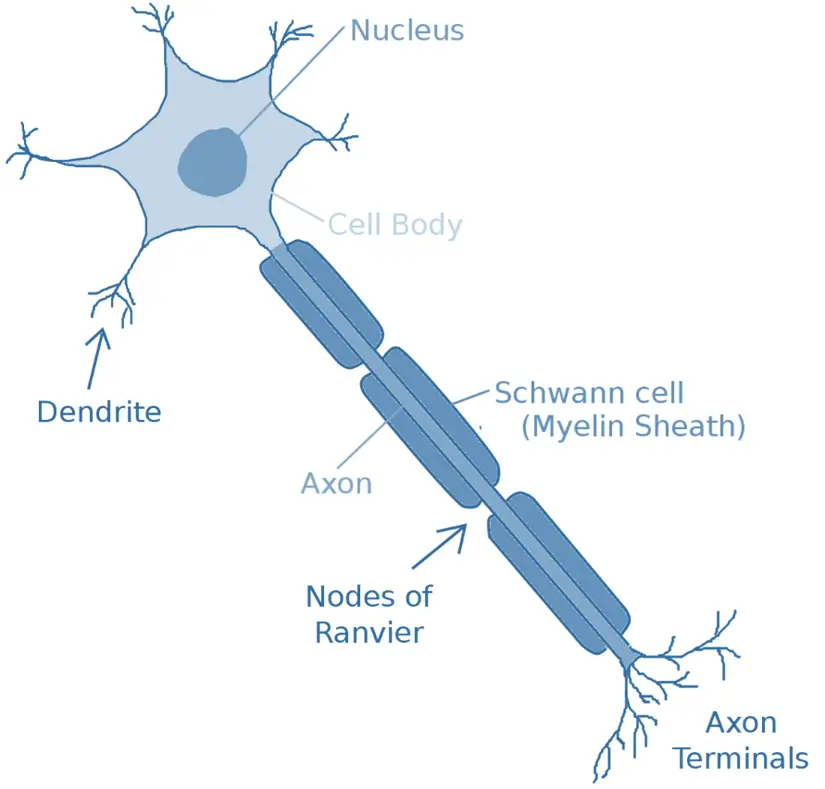
Key Parts of a Neuron
Cell Body (Soma):
- Contains the nucleus with genetic material and essential organelles for the neuron’s function.
Advertisements
Dendrites:
- Short, branch-like projections that receive signals from other neurons or sensory cells and transmit them to the cell body.
Axon:
- A long projection that transmits electrical signals (action potentials) away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Advertisements
Myelin Sheath:
- A fatty layer insulating the axon, increasing the speed of signal transmission, formed by glial cells.
Nodes of Ranvier:
- Gaps in the myelin sheath that allow rapid signal conduction through saltatory conduction.
Advertisements
Axon Terminals:
- Branches at the end of the axon that form synapses with other neurons or target cells, converting electrical signals into chemical signals (neurotransmitters).
Axon Hillock:
- The site where action potentials are initiated based on incoming signals.
Synaptic Terminals:
- Release neurotransmitters to transmit signals across synapses.
Advertisements
Synaptic Cleft:
- The gap between neurons where neurotransmitters are released for communication.
Neurotransmitter Receptors:
- Bind neurotransmitters to initiate a response in the receiving cell.
This structure allows neurons to effectively transmit information throughout the nervous system.
Advertisements

