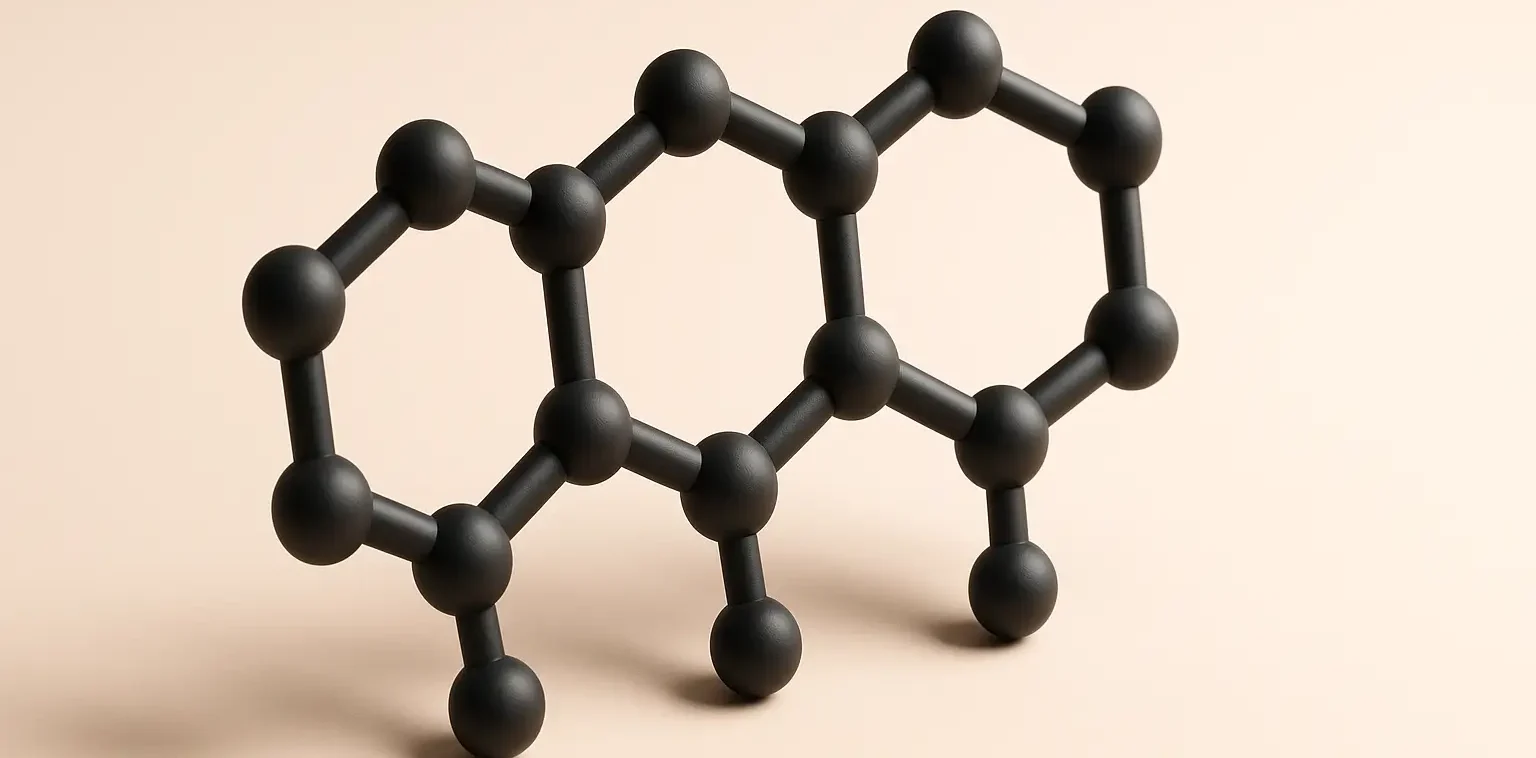
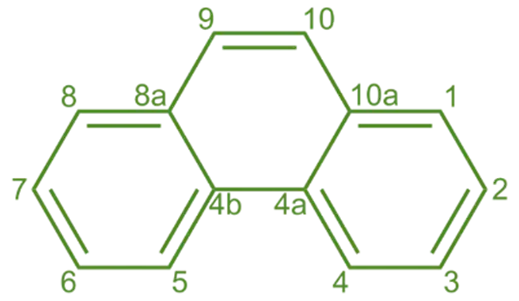
Structure of Phenanthrene:
- It is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composed of three fused benzene rings arranged in a linear arrangement.
- Its molecular formula is C14H10.
Synthesis of Phenanthrene:
-
From Coal Tar:
- It is extracted from the high boiling fraction of coal tar.
-
Laboratory Synthesis (Bardhan-Sengupta Synthesis):
- Condensation: Benzene is condensed with phthalic anhydride in the presence of aluminum chloride.
- Reduction and Cyclization: The resulting product undergoes reduction and cyclization to form phenanthrenes.
-
Benzene + Phthalic anhydride → AlCl3 (Reagent) → Phenanthrenes
Reactions of Phenanthrene:
-
Electrophilic Substitution:
- Nitration: Phenanthrenes reacts with nitric acid to form nitro phenanthrene.
-
C14H10 + HNO3 → H2SO4 (reagents) → C14H9NO2 + H2O
-
- Sulfonation: Phenanthrenes reacts with sulfuric acid to form phenanthrenes sulfonic acid.
-
C14H10 + H2SO4 → C14H9SO3H + H2O
-
- Nitration: Phenanthrenes reacts with nitric acid to form nitro phenanthrene.
-
Oxidation:
- Phenanthrenes can be oxidized to phenanthrenequinone using oxidizing agents such as chromic acid (H2CrO4).
-
C14H10 + 2[O] → C14H8(O)2
-
- Phenanthrenes can be oxidized to phenanthrenequinone using oxidizing agents such as chromic acid (H2CrO4).
Derivatives:
- Phenanthrenequinone: A derivative formed by the oxidation of phenanthrene, used in organic synthesis.
- Alkylated Phenanthrenes: Important in the study of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and environmental pollutants.
Advertisements
Medicinal Uses:
- Derivatives: Phenanthrenes derivatives, such as phenanthridine alkaloids, have been studied for their potential anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities. However, phenanthrenes itself is not commonly used in medicine due to its carcinogenic properties.