Pilot Plant:
A pilot plant is a small-scale manufacturing facility where pharmaceutical formulations developed in the laboratory are produced under real-world conditions.
It is designed to mimic the full-scale production process, allowing researchers and engineers to validate and optimize manufacturing protocols, assess scalability issues, and ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) before commercial-scale production.
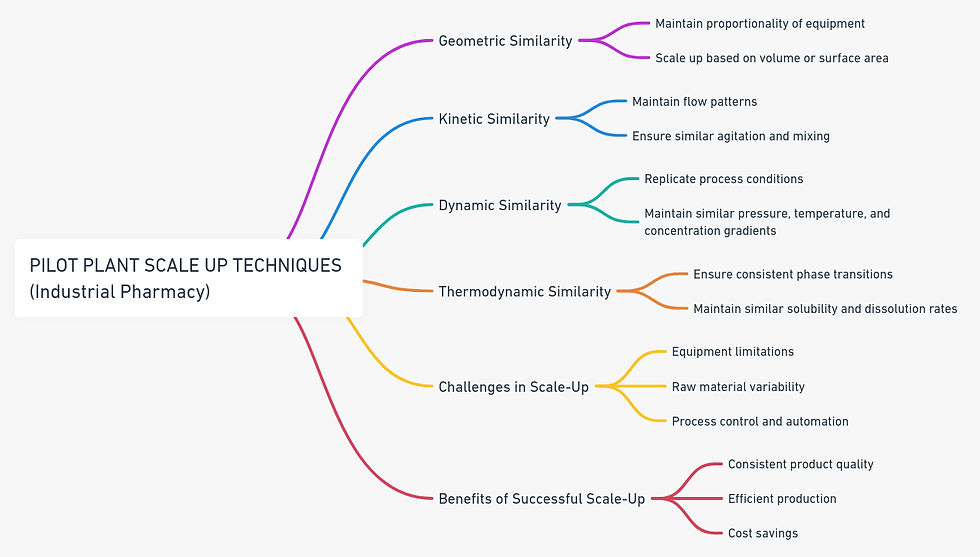
Scale-Up Techniques:
Scale-up techniques refer to the systematic methods used to increase the production volume of a pharmaceutical formulation from laboratory scale to pilot plant scale, and eventually to commercial manufacturing scale.
These techniques involve adjusting process parameters, equipment configurations, and formulations to ensure consistent quality, efficacy, and safety of the product as production volumes increase, while also meeting regulatory requirements.
Objective of pilot plant:
1. Bridge the Gap:
Transition from laboratory-scale development to commercial-scale production smoothly.
2. Process Validation and Optimization:
Test and optimize the manufacturing process under real-world conditions.
3. Quality Assurance:
Ensure product quality and consistency as production volumes increase.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
Generate data and documentation necessary for regulatory submissions and ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
5. Risk Mitigation:
Identify and address potential scalability and production issues early, minimizing risks associated with large-scale production.
6. Cost Control:
Optimize processes and troubleshoot issues in a smaller, more cost-effective environment before full-scale manufacturing.
7. Stability Testing:
Produce sufficient quantities of the product for conducting stability and other necessary tests.
8. Training and Skill Development:
Provide a platform for training personnel in a setting that mimics commercial manufacturing conditions.