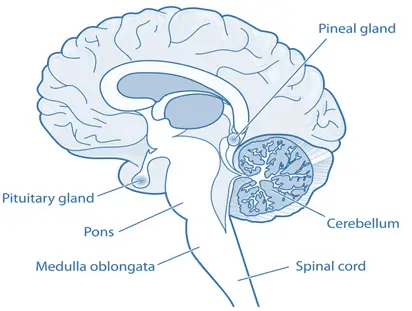
- The pineal gland is a small, pea-shaped endocrine gland located in the brain, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two rounded thalamic bodies join.
- Despite its small size, the pineal gland plays a significant role in the regulation of various body functions, especially related to the sleep-wake cycle and hormonal balance.
Advertisements
Structure of Pineal gland
-
Location:
- The gland is situated deep in the brain, in the epithalamus, near the midline, positioned between the two cerebral hemispheres.
-
Appearance:
- It is reddish-gray and about the size of a grain of rice (approximately 5-8 mm in length).
-
Composition:
- The gland is made up of pinealocytes (the main cells responsible for the production of melatonin) and supportive glial cells.
Function of Pineal gland
- The primary function of gland is to secrete melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythms, essentially the sleep-wake cycle.
- Melatonin production is influenced by the detection of light by the retina; it is secreted in response to darkness and inhibited by light.
- Melatonin Secretion: Increases in the absence of light, signaling the body to prepare for sleep.
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Helps synchronize the circadian rhythm to the natural light-dark cycle of the environment.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): The pineal gland’s function is also thought to be related to seasonal affective disorder, as the amount of daylight affects melatonin levels.
Advertisements
Disorders of Pineal gland
-
Pineal Cysts:
- Small, benign fluid-filled sacs, often asymptomatic but large cysts can cause headaches or vision problems.
-
Pineal Tumors:
- Tumors like pineal germinomas or pinealocytomas can disrupt melatonin production or cause neurological symptoms due to pressure on nearby brain structures.
-
Sleep Disorders:
- Disruptions in melatonin production can lead to sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or irregular sleep patterns.
-
Effect on Puberty:
- The pineal gland may influence the timing of puberty. Disorders affecting melatonin could potentially impact its onset, though more research is needed.
Treatment of Pineal gland
- Treatment for gland disorders depends on the specific condition and its severity.
- Management strategies may include:
- Observation: Many pineal cysts are monitored for changes in size or symptoms over time.
- Surgery: For tumors or cysts causing symptoms, surgery might be necessary to remove the growth or relieve pressure on surrounding brain structures.
- Medication: For sleep disorders related to melatonin production, melatonin supplements might be prescribed to help regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
- Radiation Therapy: In some cases of pineal tumors, radiation therapy may be used as part of the treatment plan.
- Given its role in regulating sleep and potentially other endocrine functions, the pineal gland, despite its small size, has a significant impact on human health and well-being.
Advertisements

