Principle of Pitot Tube:
- Based on Bernoulli’s theorem. Measures the difference between the stagnation pressure and static pressure to determine fluid velocity.
Formula:
$v = \sqrt{\frac{2\Delta P}{\rho}}
$
- Where:
- v = flow velocity
- ΔP = difference between stagnation pressure and static pressure
- ρ = fluid density
Construction of Pitot Tube:
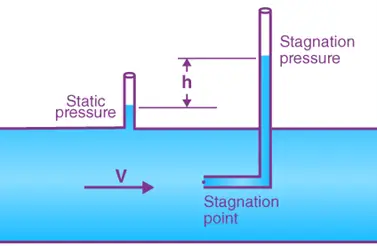
- Pitot Tube: L-shaped tube with an opening facing the flow.
- Static Ports: Small holes on the side of the tube to measure static pressure.
- Manometer: Measures the pressure difference between the stagnation and static pressures.
Working of Pitot Tube:
- The fluid enters the tube, stagnating and creating a high-pressure region.
- Static pressure is measured from the ports on the side.
- The difference between the stagnation and static pressures is used to calculate the fluid velocity.
Uses:
- Measuring the velocity of air in HVAC systems.
- Used in aircraft to measure airspeed.
- Applied in wind tunnel testing and river flow measurements.
Advantages:
- Simple and inexpensive.
- Can measure high-speed flows.
- Minimal disturbance to the flow.
Disadvantages:
- Accuracy can be affected by misalignment with the flow direction.
- Limited to point measurement (not for varying velocity profiles).
- Requires careful calibration and maintenance.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

