- Preparation of Alcohols can be prepared via various chemical reactions.
- Here’s is a Preparation of Alcohols structured explanation of the primary methods, detailing the process, type of reaction, and examples.
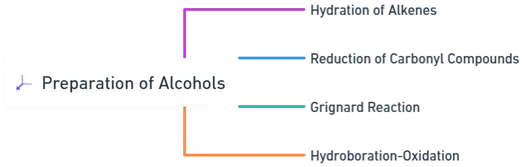
Hydration of Alkenes for Preparation of alcohols
-
Process and Reaction Type:
- Alkenes undergo hydration, an electrophilic addition reaction, where water is added across the double bond in the presence of an acid catalyst (often sulfuric acid, H2SO4) to form alcohols.
-
Chemical Reaction:
- R2C=CR2 + H2O → R2CHOH-R2
-
Example:
- CH2=CH2 + H2O → CH3CH2OH
- (Ethylene reacts with water to form ethanol.)
Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds
-
Process and Reaction Type:
- Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols, respectively, using reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or sodium borohydride (NaBH4).
- This is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
-
Chemical Reaction (using LiAlH4):
- RC(O)R′ + LiAlH4 → RCH(OH)R′
-
Example:
- CH3CHO + LiAlH4 → CH3CH2OH (Acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol.)
Grignard Reaction
-
Process and Reaction Type:
- The Grignard reaction involves the reaction of a Grignard reagent (RMgX, where R is an alkyl or aryl group, and X is a halogen) with an aldehyde or ketone.
- The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon to form an alcohol after hydrolysis.
-
Chemical Reaction:
- R-Mg-X+R′-C=O → R-R′-C-O-Mg-X → R-R′-C-OH + MgXOH
-
Example:
- CH3-Mg-Br + CH3CHO → CH3CH2-O-Mg-Br → CH3CH2OH + MgBrOH
- (A Grignard reagent reacts with acetaldehyde to produce ethanol.)
Hydroboration-Oxidation
-
Process and Reaction Type:
- This method involves the addition of borane (BH3) to an alkene to form a borane-alkene complex, followed by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of a base, leading to the formation of alcohols.
-
Chemical Reaction:
- R2C=CR2 + BH3 → R2CHO-BH2
- R2CHO-BH2 + H2O2+OH− → R2CHOH + B(OH)3
-
Example:
- CH3CH=CH2 + BH3 → CH3CH2CH2-BH2
- CH3CH2CH2-BH2 + H2O2 + OH− → CH3CH2CH2OH + B(OH)3
- (Propene is converted to propanol via hydroboration-oxidation.)
- Each method offers a unique approach to synthesizing alcohols, providing versatility in organic synthesis depending on the desired alcohol and the available starting materials