Principle of Rotameter:
- Based on the variable area principle.
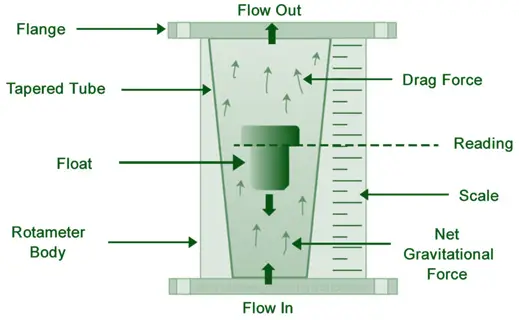
- A float rises in a tapered tube until the area between the float and the tube balances the gravitational force on the float.
- The flow rate is directly read from a scale on the tube.
Construction of Rotameter:
Advertisements
- Tapered Tube: Vertically mounted, widens from bottom to top.
- Float: Moves freely within the tube, indicating the flow rate based on its position.
Working of Rotameter:
- Fluid enters the bottom of the tapered tube, causing the float to rise.
- The float stabilizes at a position where the upward force from the fluid equals the weight of the float.
- The height of the float is read against a scale to determine the flow rate.
Advertisements
Uses:
- Measuring the flow rate of gases and liquids in laboratory and industrial settings.
- Common in medical devices, water treatment plants, and chemical processing.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for opaque fluids as the float position is not visible.
- Limited to specific flow ranges and not suitable for very high flow rates.
- Calibration can be affected by changes in fluid density and viscosity.
Advertisements

