Principle of Simple Distillation:
- This distillation separates components of a mixture based on differences in their boiling points, typically when the boiling points differ significantly (more than 25°C).
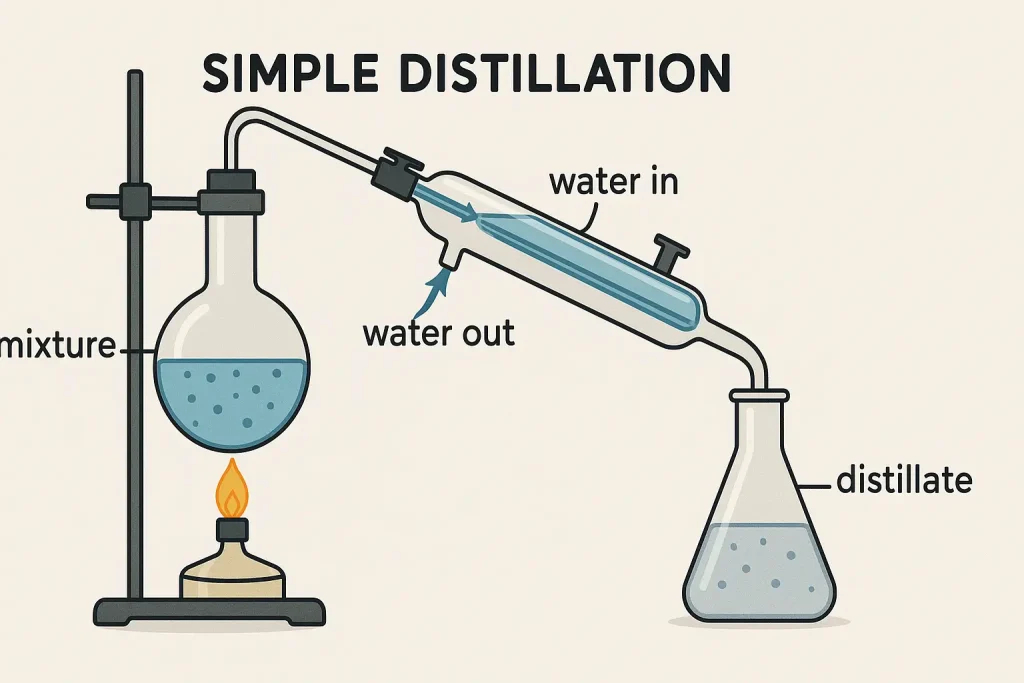
Methodology:
- Setup: Consists of a distillation flask, a heat source, a condenser, and a receiving flask.
- Heating: The mixture is heated in the distillation flask.
- Vaporization: The component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first.
- Condensation: The vapor passes through the condenser, where it cools and condenses back into a liquid.
- Collection: The condensed liquid (distillate) is collected in the receiving flask.
Uses:
- Purification of solvents.
- Separation of volatile components from non-volatile impurities.
- Distillation of water.
Merits:
- Simple and straightforward setup.
- Cost-effective for small-scale operations.
- Suitable for separating mixtures with significantly different boiling points.
Demerits:
- Inefficient for mixtures with close boiling points.
- Limited to batch processes.
- Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials that decompose at high temperatures.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

