Buy Now the Hard Copy of notes for seamless and ad-free learning, Click Below!
The Sorensen’s pH scale is a numerical representation of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
It was introduced by Danish chemist Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen in 1909.
Sørensen developed this scale to simplify the expression of hydrogen ion concentrations in solutions, which can vary over a wide range.

Definition of pH
The term "pH" stands for "potential of hydrogen" and is defined mathematically as:
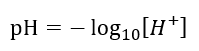
Where:
[H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
Logarithmic Nature
The logarithmic scale means that each whole number change in pH represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
For example, a solution with a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than one with a pH of 4.
Scale Range
The pH scale typically ranges from 0 to 14:
Acidic Solutions: pH < 7
Neutral Solutions: pH = 7
Basic (Alkaline) Solutions: pH > 7
Importance of Sorensen’s pH Scale
The pH of a solution affects chemical reactions, biological processes, and the solubility of compounds.
It is crucial in various fields, including:
Chemistry
Biology
Medicine
Agriculture
Environmental Science
Buy Now the Hard Copy of notes for seamless and ad-free learning, Click Below!


