Tonicity
- S-1-Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry
- Feb 26
- 1 min read
Updated: Apr 12
Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution separated by a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane.
It measures the osmotic pressure gradient between the two solutions and influences the movement of water across the membrane, affecting cellular behavior.
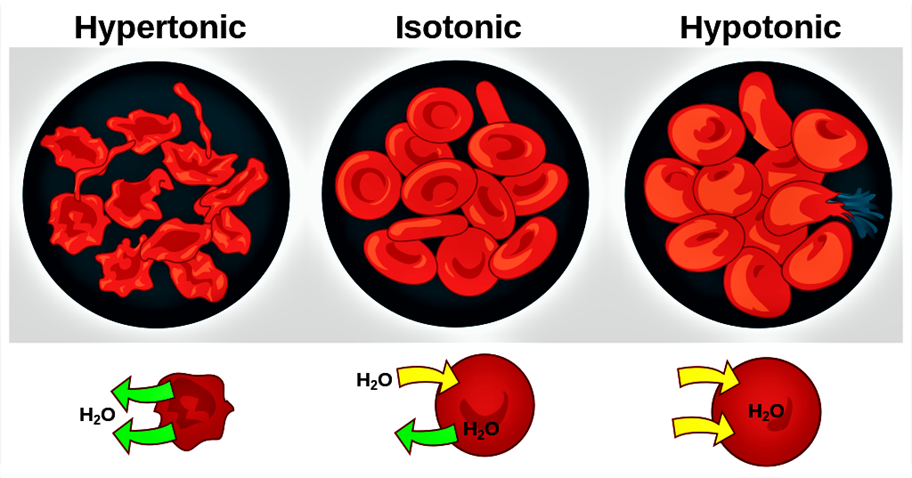
Types of Tonicities
1) Isotonic
Definition: The solution has the same osmotic pressure as the reference solution (e.g., physiological fluids like blood or tears).
Effect on Cells: No net water movement across the membrane; cells maintain their normal shape and size.
Applications: Used in medical and pharmaceutical settings to prevent osmotic stress on cells and tissues, ensuring they remain undamaged.
2) Hypotonic
Definition: The solution has a lower osmotic pressure than the reference solution.
Effect on Cells: Water moves into the cells, causing them to swell and potentially rupture if the osmotic pressure difference is significant.
Applications: Used in specific medical situations to induce cell swelling, such as in the treatment of raised intracranial pressure.
3) Hypertonic
Definition: The solution has a higher osmotic pressure than the reference solution.
Effect on Cells: Water moves out of the cells, causing them to shrink.
Applications: Utilized to reduce swelling and inflammation or to treat conditions like hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels).
Understanding tonicity is crucial for managing fluid balance in medical treatments and ensuring the proper functioning of cells in various environments.



Yorumlar