UV-Visible Spectroscopy
- S-7-INSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS
- Nov 21, 2024
- 1 min read
Overview
UV-Visible spectroscopy is a technique used to measure the absorption of light in the ultraviolet (200-400 nm) and visible (400-700 nm) regions of the electromagnetic spectrum by a sample.
This method provides valuable information about the electronic structure of molecules, particularly the presence of chromophores and their environment. It is widely utilized in:
Quantitative analysis
Identifying compounds
Studying reaction kinetics
Determining molecular concentrations
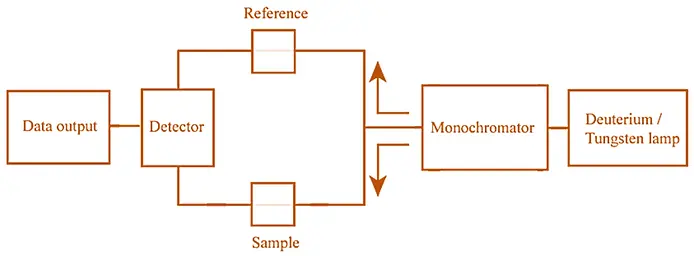
Basic Principle of UV Visible spectroscopy
When a molecule absorbs light, its electrons are excited from a lower energy orbital to a higher energy orbital.
The energy difference between these orbitals corresponds to the energy of the absorbed photon, which is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
By measuring the absorbance at specific wavelengths, various properties of the sample can be inferred.









Comments