Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker used as an anti-anginal drug that reduces heart workload and improves blood flow by relaxing blood vessels.
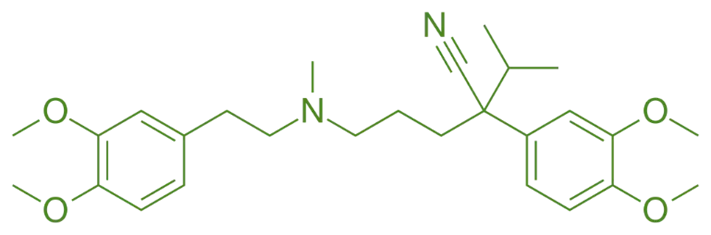
Structure of Verapamil
- Verapamil is a phenylalkylamine derivative featuring a benzene ring connected to a dihydropyridine moiety through a methoxyethyl bridge.
- Chemical Formula: C₂₂H₂₉N₃O₄
Mode of Action
- Calcium Channel Blocking: Inhibits L-type calcium channels in cardiac and smooth muscle cells.
- Negative Inotropic Effect: Decreases myocardial contractility.
- Negative Chronotropic Effect: Reduces heart rate by slowing sinoatrial node activity.
- Vasodilation: Lowers blood pressure by relaxing vascular smooth muscle.
Uses
- Hypertension: Lowers blood pressure by causing vasodilation.
- Angina Pectoris: Reduces myocardial oxygen demand and increases oxygen supply.
- Arrhythmias: Treats supraventricular tachycardias by slowing AV node conduction.
- Migraine Prophylaxis: Prevents the onset of migraines.
- Cluster Headaches: Used as a preventive measure.

